|
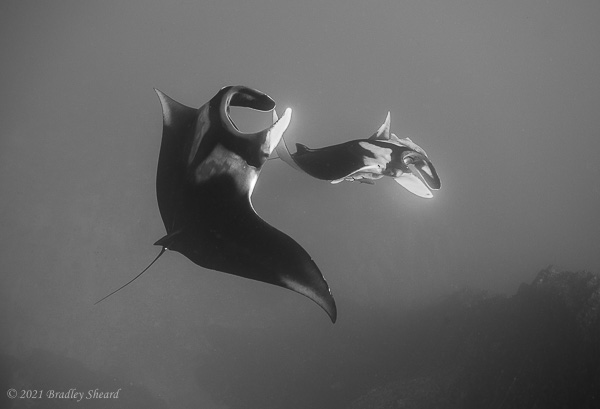
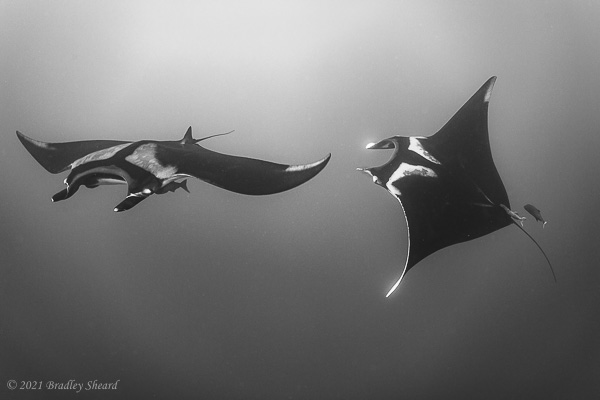
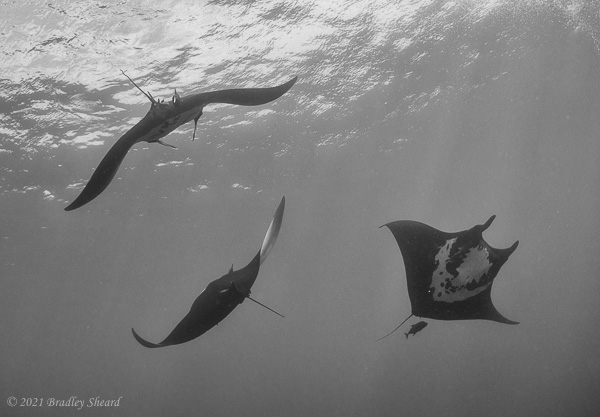
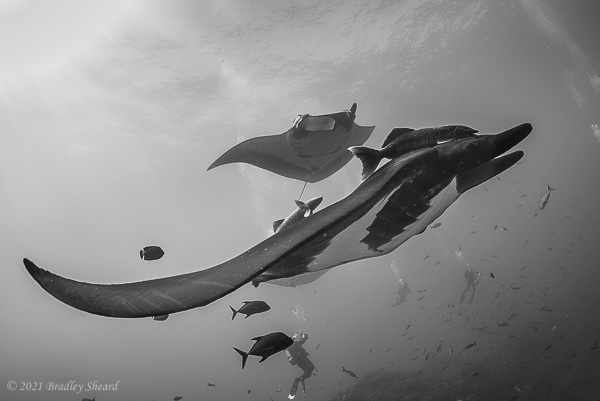
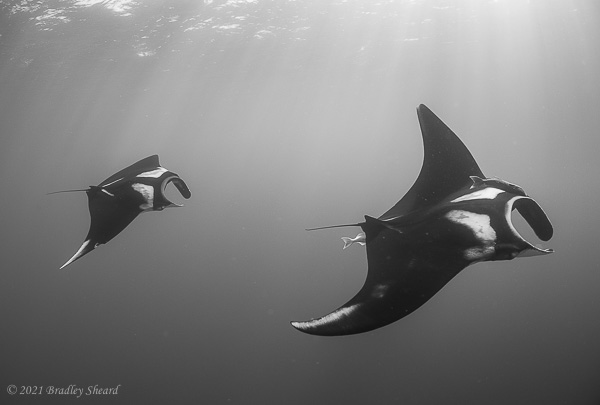
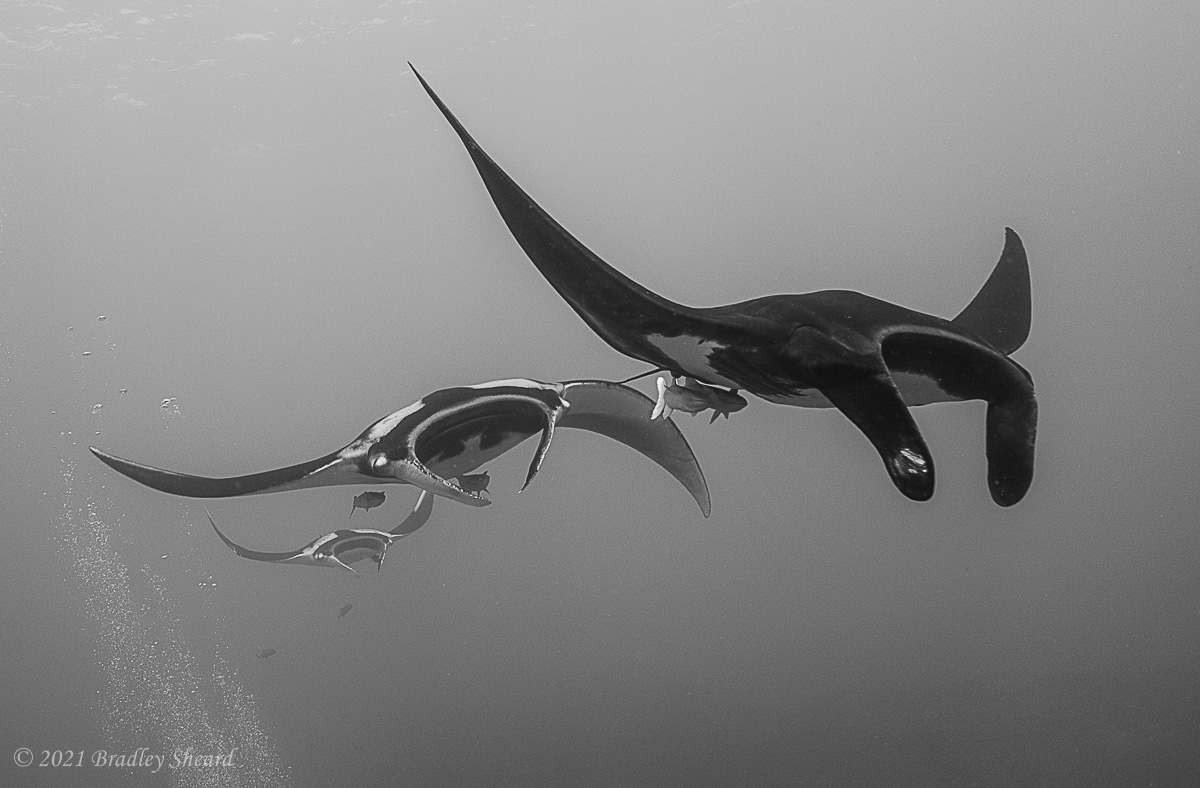
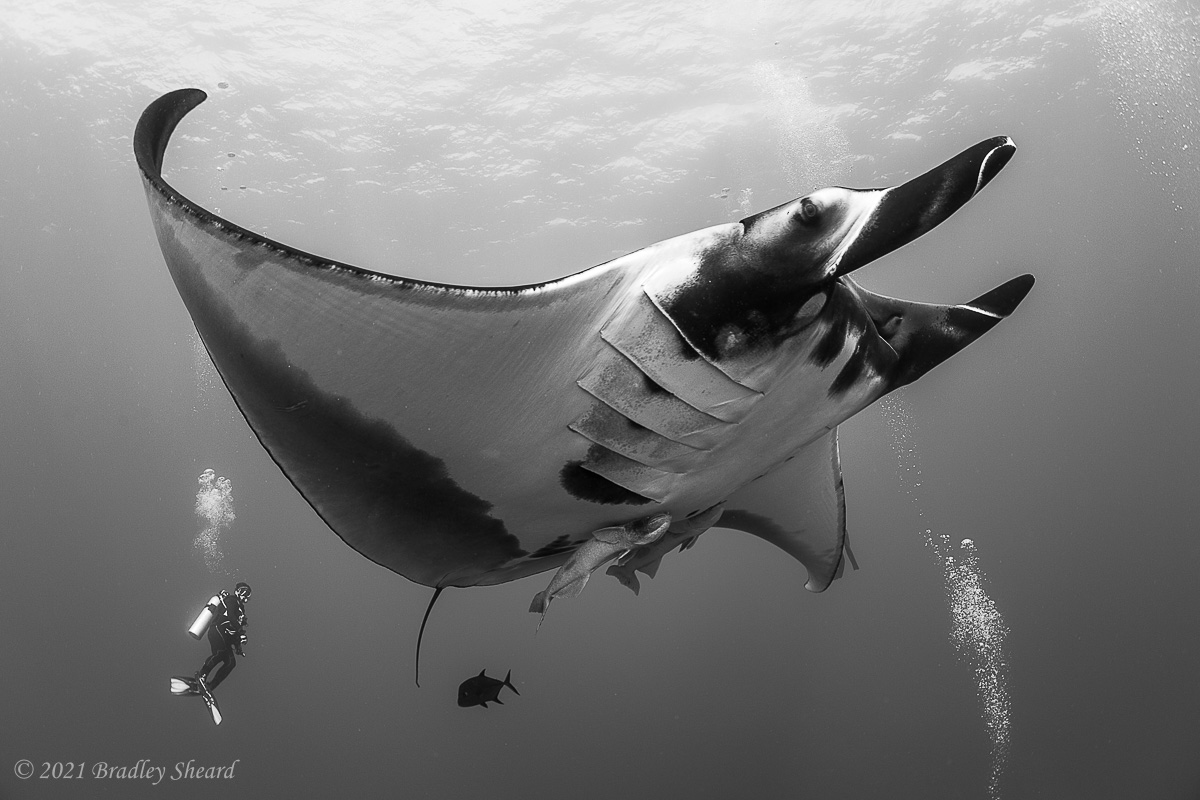
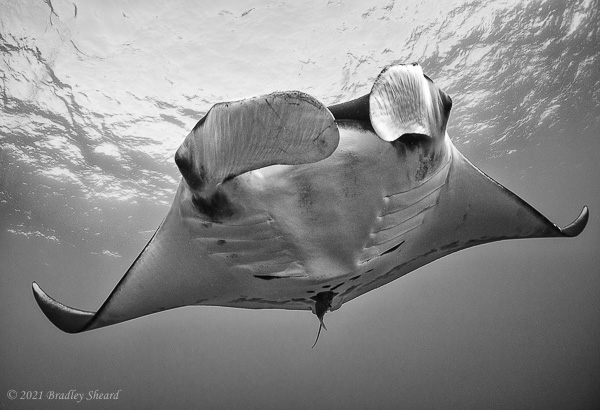
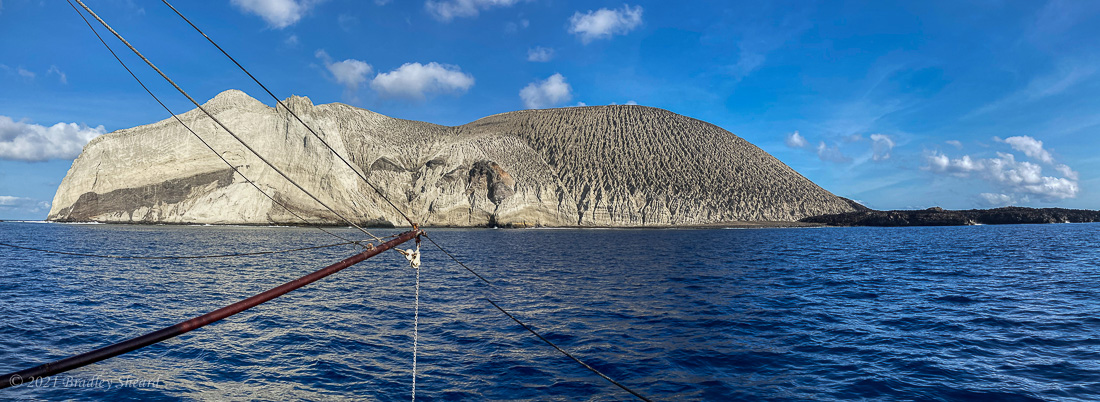
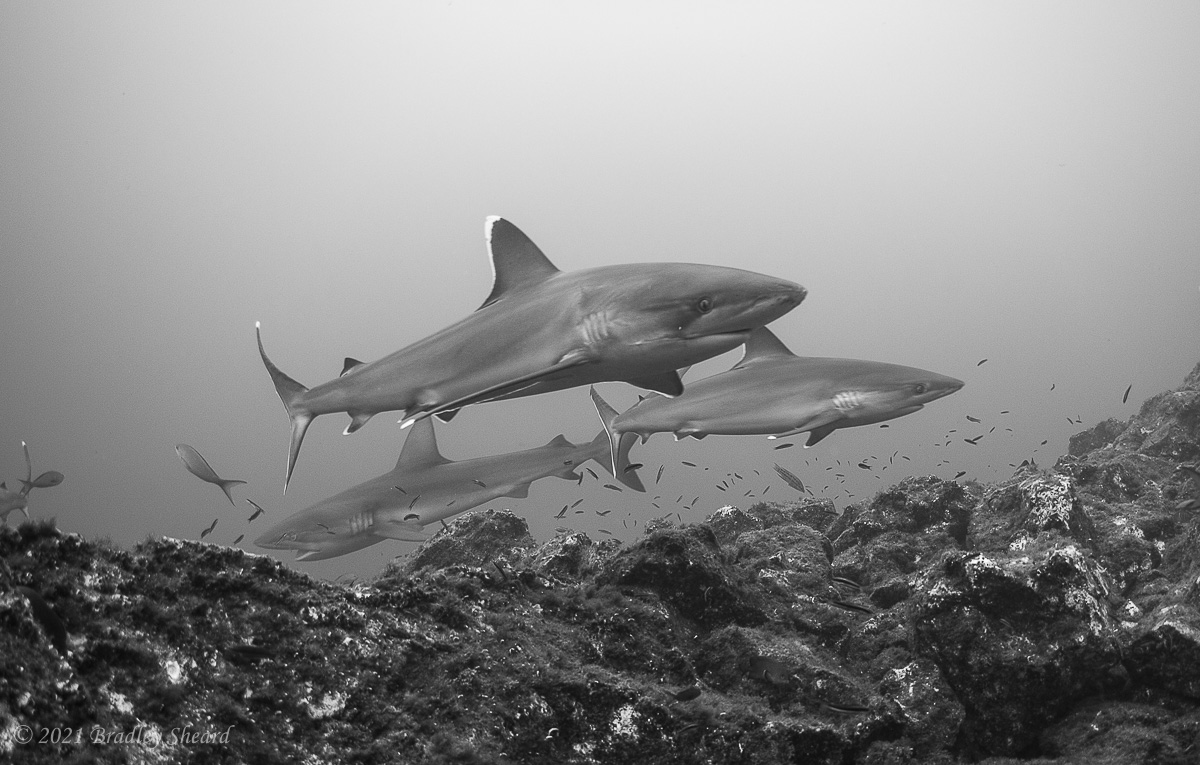
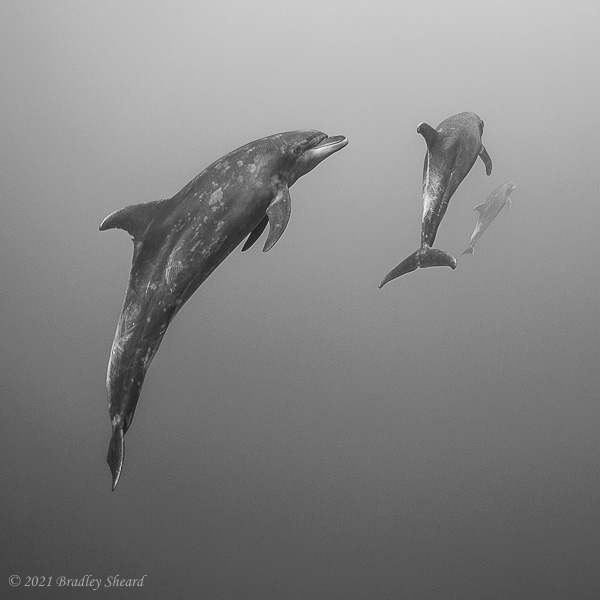
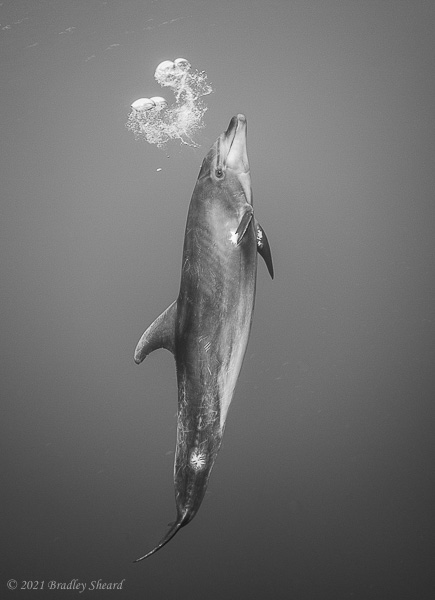
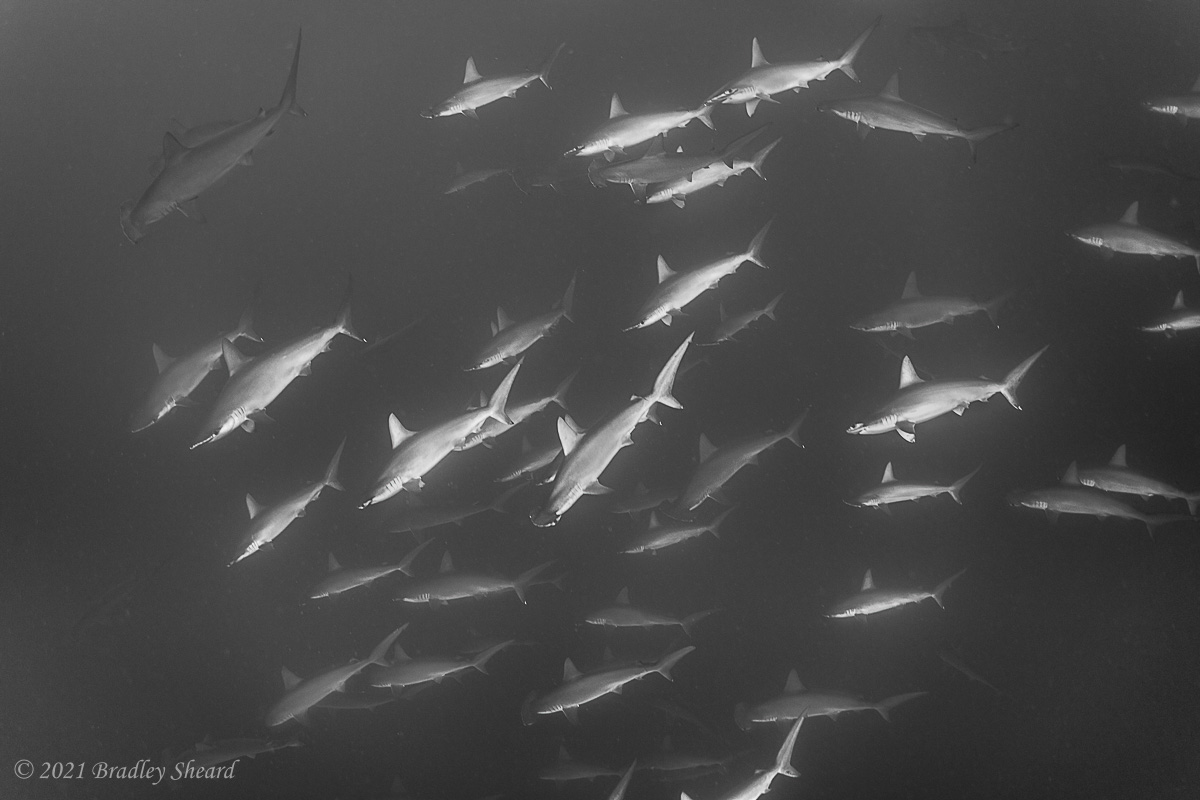
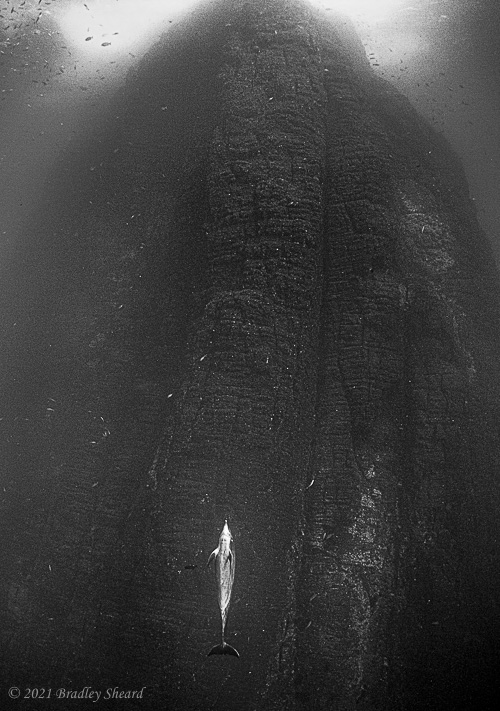
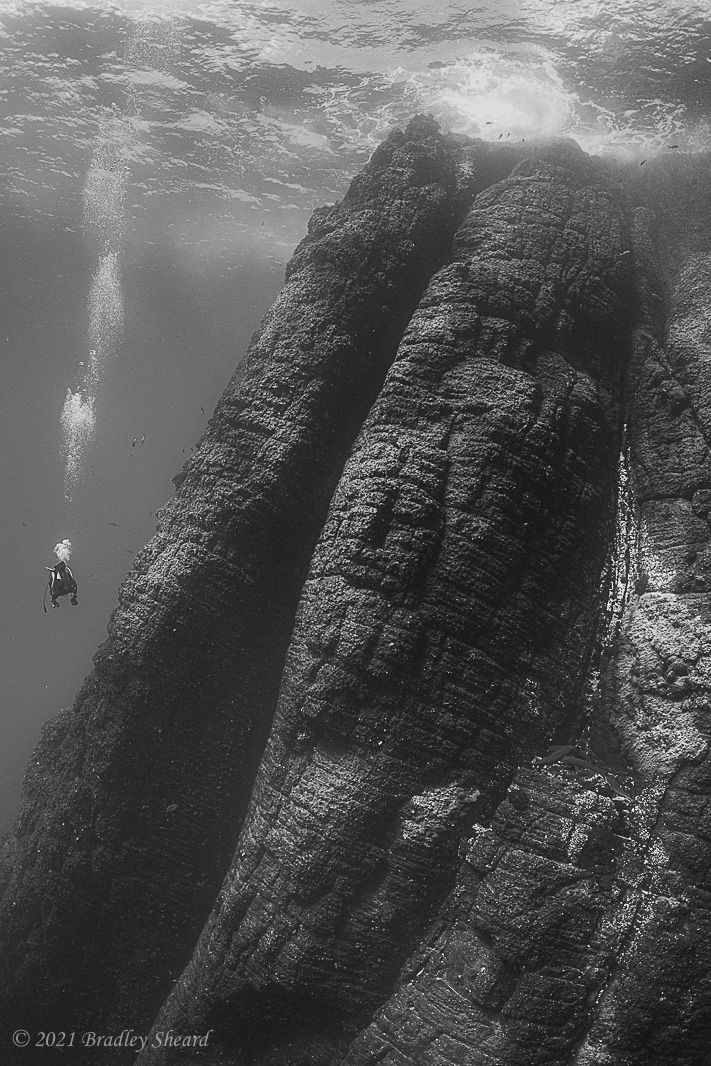
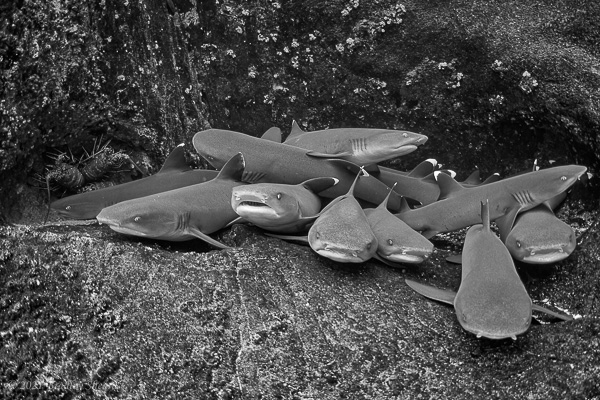
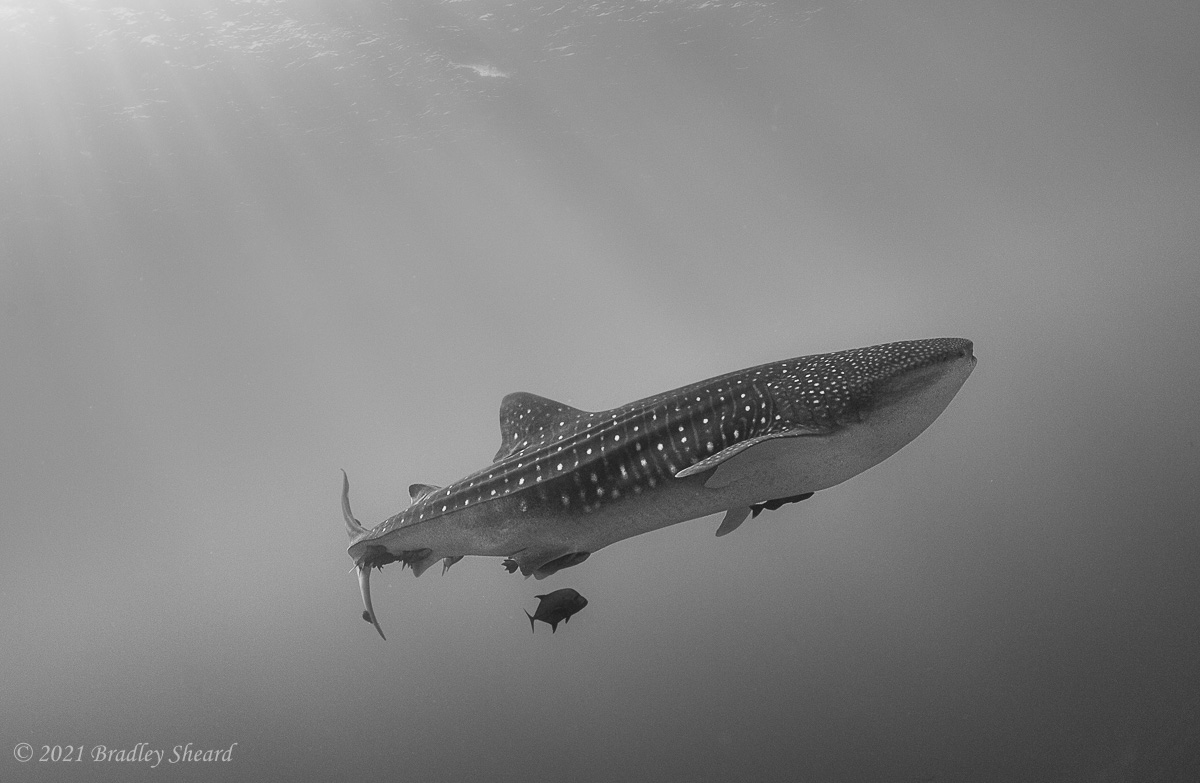
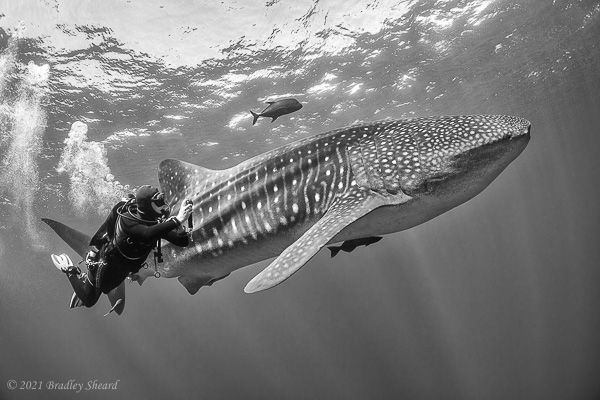
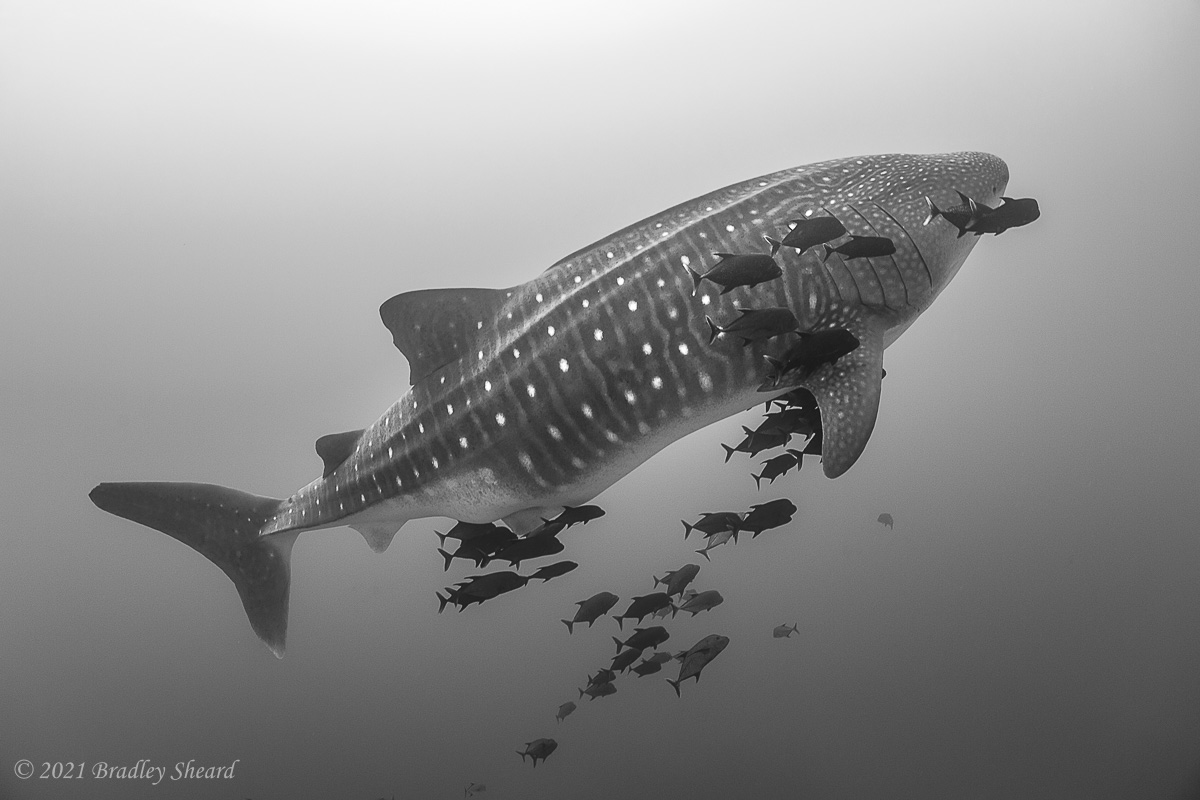
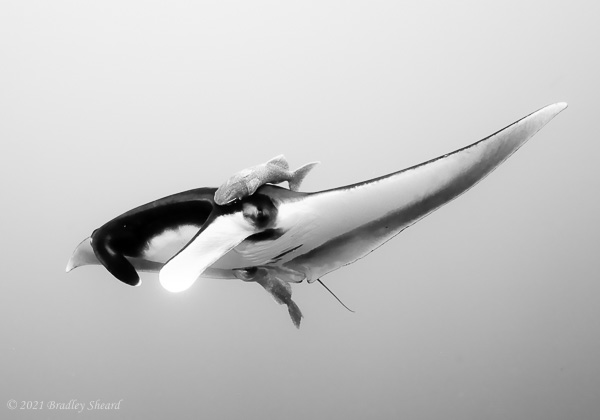
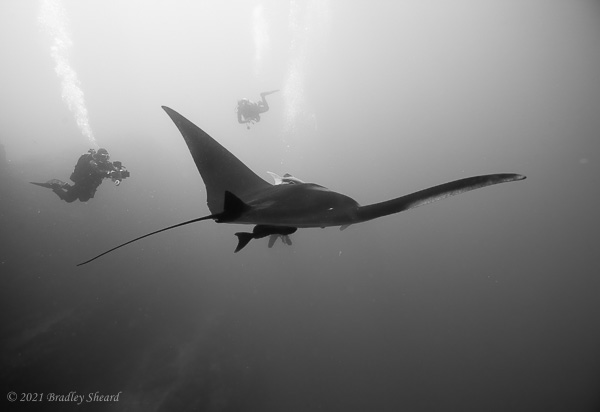
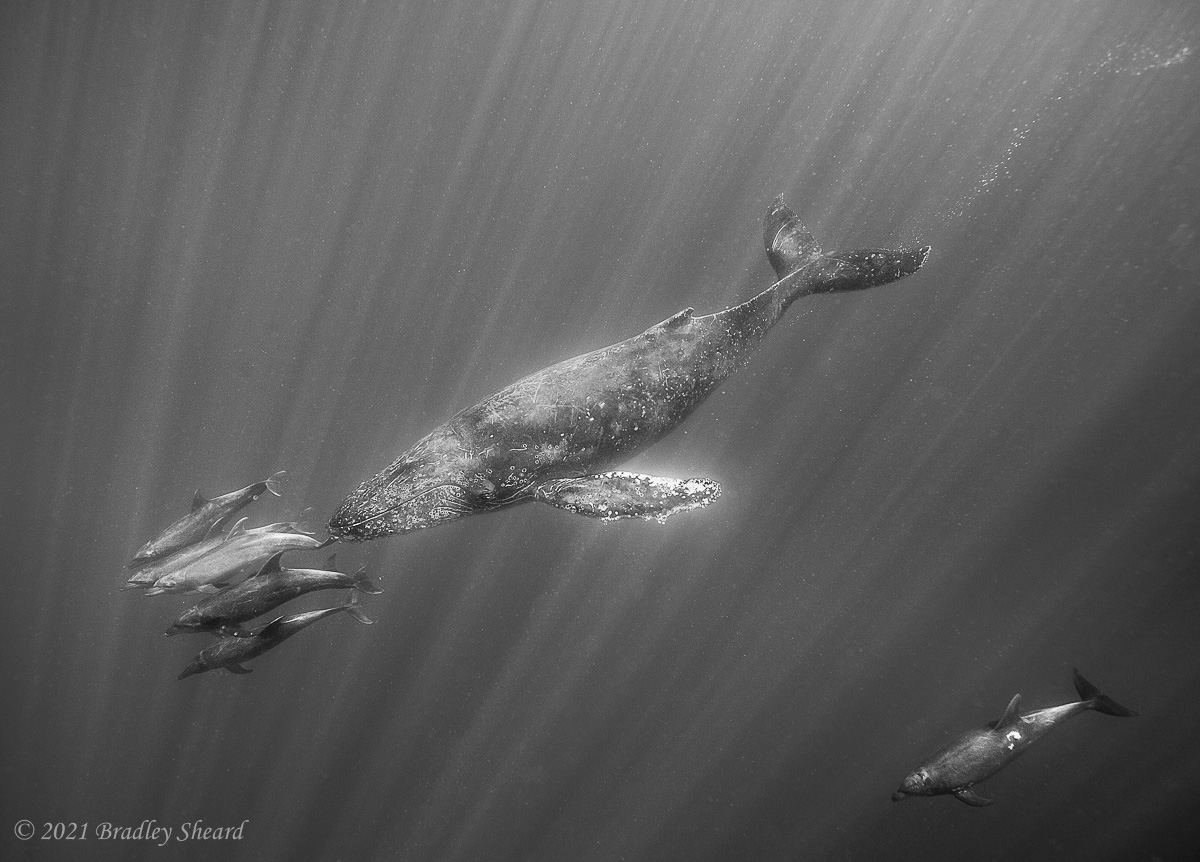
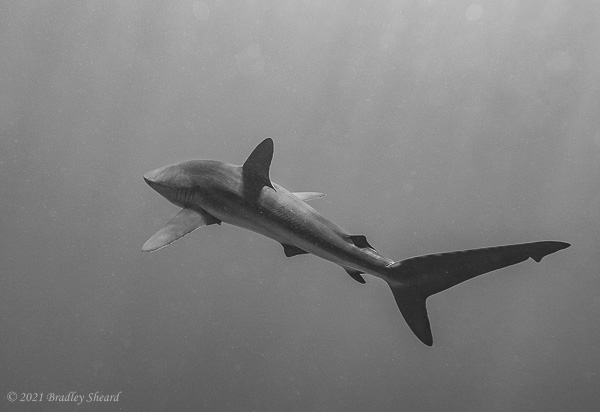
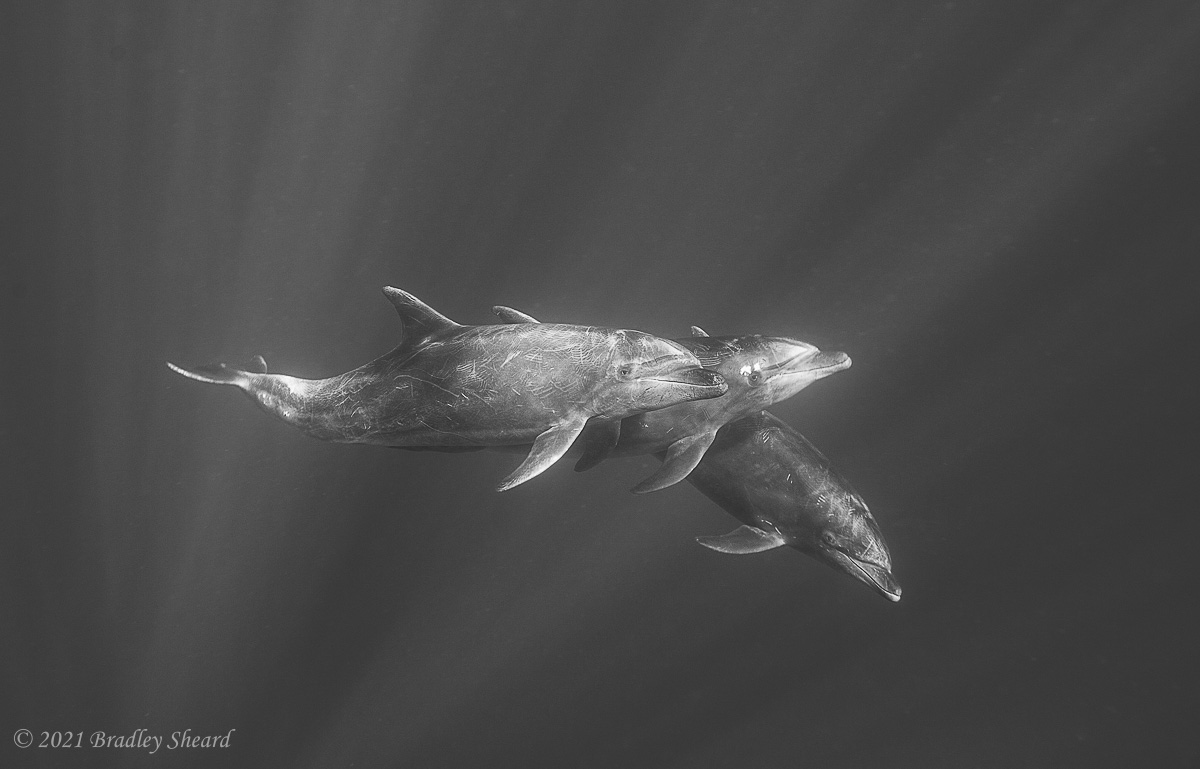
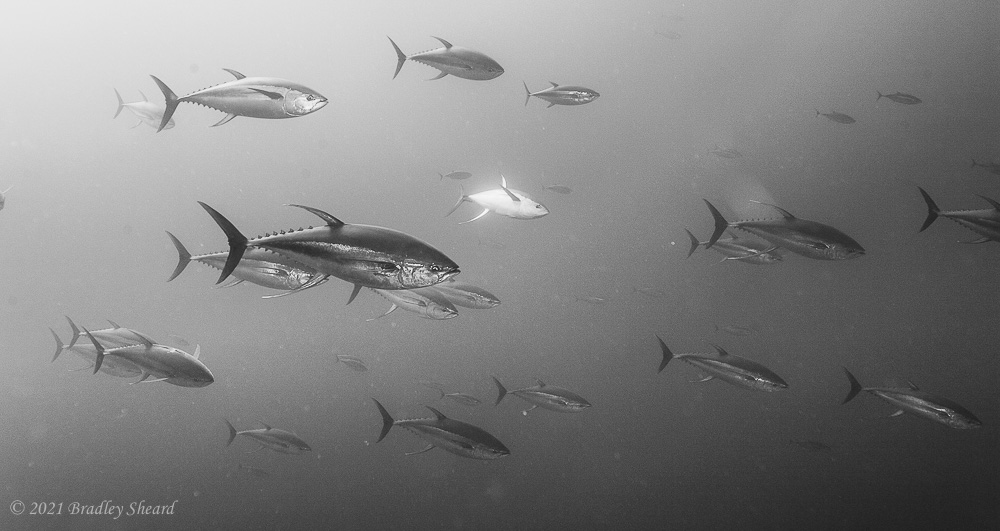
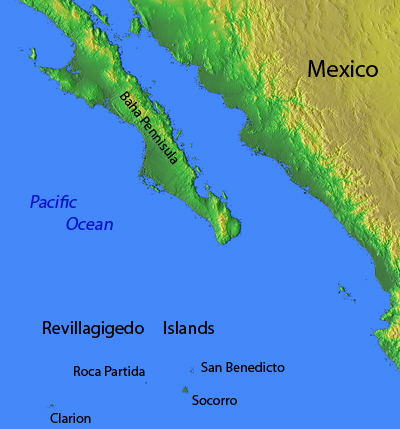
The Revillagigedo Islands, often called the Socorro Islands, are a group of largely-uninhabited volcanic islands lying approximately 250 miles southwest of Cabo San Lucas at the tip of the Baha penninsula. The archipelago is owned by Mexico, which maintains a small naval base on Socorro, the largest island in the group; the other three islands are San Benedicto, Roca Partida and Clarion. Clarion Island lies far to the west of the main group, and is seldom visited. The other three form a triangular grouping far from the Mexican mainland. The waters surrounding the islands are designated as a Mexican national protected area, and no fishing or collecting is permitted. The largest island, Socorro, measures approximately 10 miles across, while San Benedicto is much smaller, and Roca Partida is only a tiny twin-peaked rock jutting from the vastness of the Pacific, nearly 70 miles west of Socorro. Isolated from other land masses, the group of islands is sometimes referred to as the "Mexican Galapagos," possessing their own unique ecosystem. The islands isolated location and steeply sloping undersea topography causes many varieties of pelagic marine life to congregate in the surrounding waters. For divers, the islands represent an opportunity to get a close look at some of these species, including the famous manta rays, sharks, dolpins, whale sharks and, during the winter months, humpback whales. The only practical way to visit the islands is by liveaboard dive boat. | |
 |
|
| Dances with Mantas... |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |








































